Assessment Tools part 3 (KFQ, OSCE)
/ 11 min read
Part สุดท้ายสำรหับเครื่องมือการประเมินจะรวบ ทั้ง Key-feature และ OSCE มาไว้ใน part เดียวกัน
KFQ
Key-features Question เป็นรูปแบบการสอบอีกประเภทหนึ่งที่จะเน้นในจุดสำคัญๆ การตอบคำถามจะเน้นที่คำตอบที่จำเป็นสำคัญต่อการรักษา หรือความผิดพลาดที่มักจะเกิดขึ้น ก่อนที่จะออกแบบข้อสอบ KFQ ได้นั้น จะต้องทำความเข้าใจกับหลักการ Problem solving process ก่อน
Problem solving process
คือการแก้ปัญหาทาง Clinic จะมีลำดับดังนี้
- Cognitive ความรู้พื้นฐานที่จะต้องมี
- Data gathering รวบรวมข้อมูลที่จำเป็น เช่นการซักประวัติ, ตรวจร่างกาย เป็นต้น
- Hypothesis generation การตั้ง Initial diagnosis, problem list
- Investigation/interpretation เพื่อหาข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม
- Hypothesis refinement/assessment ยืนยันสิ่งที่ตั้งสมมติฐาน
- Mangement ตัดสินใจให้การดูแล รักษา
- Patient education ให้ความรู้แก่ผู้ป่วย
- Basic clinical sciences เชื่อมโยง Basic Science เช่น Pathophysiology, Biomolecule เป็นต้น
จาก Problem solving process ข้างต้นจะพบว่ามีหลายขั้นตอนในการแก้ปัญหาทาง Clinic แต่การออกแบบข้อสอบ Key-features จะไม่่ได้เน้นทุกขั้นตอนเหมือน MEQ จะเน้นเฉพาะที่เป็นจุดวิกฤติ, มักผิดพลาด หรือทำให้สับสนบ่อยๆ เป็นต้น
ตัวอย่าง
A 8-year old boy presents with 4-day high grade fever, malaise.
PE: BT 38 C, BP 90/70. PR 120/min., flush face, congested conjunctiva,
skin- petechial hemorrhage, liver 2-cm below right costal margin with tenderness.| Question series A | Question series B |
|---|---|
| 1. What are the pertinent data? | 1. What is the most likely diagnosis? |
| 2. What is the most likely diagnosis? | 2. What are the appropriate investigation |
| 3. What are the appropriate investigations and reasons or expected findings? | 3. What is the appropriate management? |
| 4. What is the appropriate management? |
จากตัวอย่างข้างต้นจะเห็นว่าคำถาม Series A และ B มีความแตกต่างกันชัดเจน โดย Series A จะถามเป็นขั้นตอน พร้อมให้รายละเอียด หรือเหตุผลประกอบ แต่ B จะเน้นที่จุดสำคัญๆ ของโรคที่จำเป็นจะต้องรู้ และไม่ควรทำผิดพลาด ไม่จำเป็นต้องให้รายละเอียดการคิดในคำตอบ ซึ่งถือเป็นลักษณะของข้อสอบ Key-features
Definition
KFQ หรือ Key-features questions เป็นข้อสอบเน้นที่การตัดสินใจว่าจะทำอะไร ส่วน clinical thinking หรือ reasoning ซึ่งจะต้องผ่านกระบวนการคิดนี้อยู่แล้วไม่จำเป็นต้องแสดงออกมาให้เห็น
เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับข้อสอบ MCQ และ CRQ ข้อสอบ KFQ จะอยู่ตรงกลางระหว่างข้อสอบ 2 ชนิดนี้ คือยังสามารถออกแบบให้เขียนได้ หรือออกแบบเป็นตัวเลือกให้นำมาเติมได้
What is Key-features
Key-features ในนิยามของการแก้ปัญหา (Problem) คือส่วนสำคัญที่จะนำไปสู่การ แก้ปัญหา (Resolution of problem) เช่น
Clinical clues
ตัวอย่าง Clinical clues ที่เป็น Key-features
ตั้งปัญหา (Problem) ที่ผู้ป่วยมีอาการ Headache นำไปสู่การวินิจฉัยที่ไม่ควรพลาดคือ Subarchanoid Hemorrhage (Think of SAH) เพราะฉะนั้น Key-feautres ในที่นี้จะเป็นลักษณะ clinical clues ต้องหา Red flag signs ของอาการปวดศีรษะที่บ่งถึง Intracranial hemorrhage
Investigative procedure
ในด้าน Investigation ที่เป็นลักษณะ Key-features อาจเป็น Lab สำคัญที่ควรตรวจ หรือ Error ในการตรวจ แปลผลที่พบบ่อย ตัวอย่างเช่น ตั้งปัญหาคือ Acute Alteration of consciousness (AOC) ในผู้ป่วย Diabetes mellitus จะต้องไม่ลืมที่จะนึกถึงภาวะ Hypoglycemia ซึ่งเป็นภาวะที่ทำให้เกิด AOC และมีอันตรายต่อชีวิตได้ Key-features จะเป็นการ Investigation ที่สำคัญจะต้องทำคือ การตรวจเช็คระดับน้ำตาลในเลือด (Blood sugar)
Therapeutic Measure
การรักษาที่สำคัญเป็นอีกจุดหนึ่งที่ถูกถามบ่อยในข้อสอบที่มีลักษณะของ Key-features เนื่องจากมักจะเป็น Management ที่เป็น critical ต้องทำ หรือห้ามทำ ตัวอย่างเช่น ผู้ป่วยมีปัญหา Ventricular fibrillation (VF) แนวทางการรักษาจะต้องรีบจัดการ VF ให้เร็วที่สุดเนื่องจากเป็นภาวะอันตรายถึงชีวิต (Life threathing condition) Key-features คือ Management ให้การรักษาด้วยการ Cardioversion ไม่ว่าะจะเป็น Medical หรือ Electrical cardioversion
Characteristic of KFQ
สิ่งที่ควรนำมาใช้เป็นข้อสอบ KFQ
- A critical or essential step(s) in the resolution of a problem เป็นเรื่องที่ดู serious เช่น ตายหรือไม่ตาย
- A step(s) in which examinees are most likely to make errors in the resolution of the problem วินิจฉัยผิดบ่อยๆ investigation ผิดบ่อยๆ หรือ management ผิดบ่อยๆ
- _A difficult or challenging aspect in the identification and management
How to create KFQ
All key-feature answers are correct answers but not all correct answers are key-feature answers.
Question
การตั้งคำถามสำหรับ Key-features นั้นควรจะเริ่มจากลักษณ์สำคัญของสถานการณ์ที่จะเป็น Key-features ได้แนวทางที่พอจะช่วยเลือกปัญหาหรือ scenario ที่จะนำมาทำเป็น KFQ ดังนี้
- วางแผน หาโรคที่อยู่ใน 3 กลุ่มหลัก คือ critical, common errors และ difficult cases
- ต้องมี scenario แล้วต่อด้วยคำถาม 2-3 ข้อ
- คำถามต้องเน้นที่ clinical decision และการกระทำ ต้องไม่ถาม clinical reasoning แต่ต้องทำให้เกิด clinical reasoning เอง
- คำถามจะต้องถามเฉพาะจุดที่เป็น key-features ของ scenario หรือปัญหานั้นๆ
Answer
ลักษณะการตอบคำถาม KFQ สามารถมีได้ 2 ลักษณะใหญ่ๆ คือ Write-In และ Short Menu
- Write-In ให้นักเรียนใส่คำตอบเข้ามา
- Short Menu มีตัวเลือกให้ แต่ ไม่ใช่ 1 best answer เปรียบเทียบ MCQ จะคล้ายๆ extended matching ควรจะมีตัวลวง 2-3 เท่า แต่ต้อง possible
Write-in
- กำหนดว่าจะเขียนตอบได้กี่คำตอบ หากตอบเกินให้มี Punishment
- Management อาจจะกำหนดไม่ได้ว่าจะมีกี่ข้อ เพราะใน real situation ก็ไม่มีการกำหนด อาจจะแก้ด้วยการให้ short menu มาเป็นตัวเลือก
OSCE
การประเมินด้าน Performance ของนักเรียน จะต้องสามารถประเมินความสามารถที่แสดงออกมาได้ เมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับ Miller’s pyramid of learning
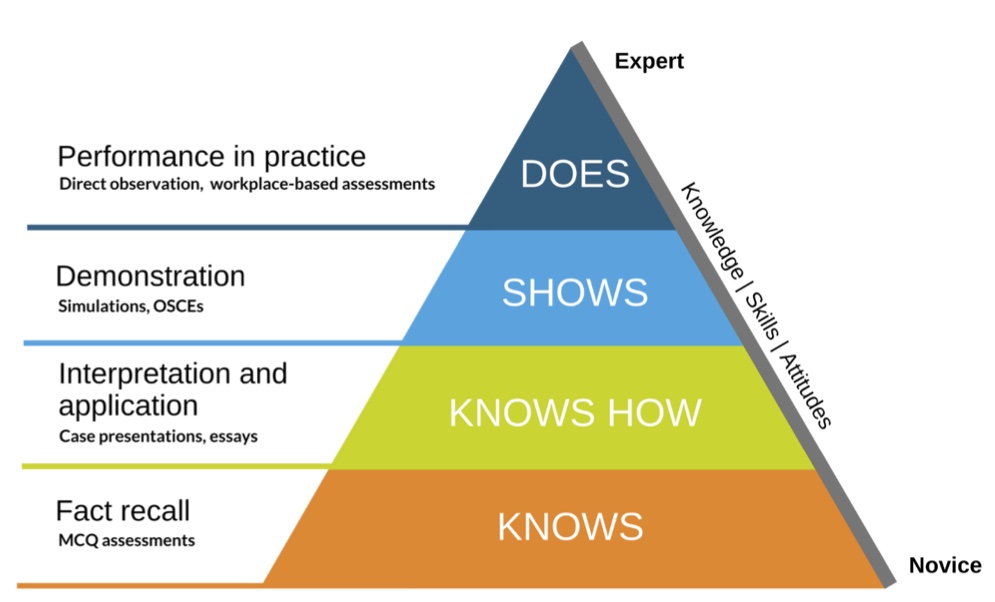
การประเมินจะต้องเป็นการประเมินให้ถึงระดับ SHOW ขึ้นไป โดยต้องคำนึงถึงปัจจัยที่ส่งผลกระทบต่อ Performance ซึ่งมีอยู่มากมายดังรูปด้านล่าง

Model of the Competency-based assessment of performance

จากรูปดังกล่าวข้างต้นจะเห็นว่าสามารถเลือกใช้เครื่องมือการประเมินได้หลากหลายอย่าง เช่น หากต้องการประเมินแบบสังเกตการณ์ ภายใต้สถานการณ์จำลองจะพบว่าเครื่องมือที่เหมาะสมจะเป็น OSCE แต่หากจะต้องประเมินภายใต้สถานการณ์การทำงานจริงจะต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น DOPS หรือ Mini-Cex เป็นต้น
เพราะฉะนั้นการเลือกเครื่องมือใจการประเมินจึงเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่ผู้สอนต้องพึงระลึกไว้เสมอว่าจะเหมาะสมกับการประเมินด้านใด และภายใต้สถานการณ์แบบใด
Definition
OSCE = “Objective structured clinical examination”
เริ่มให้ Definition ปี 1988
การสอบ clinical competency โดยแต่ละ station จะเน้นการประเมินคนละด้าน และการจัดการสอบควรมีหลาย station เพื่อประเมินหลายๆ ด้าน
_การประเมินความสามารถตาม Miller’s pyramid ต้องประเมินทั้ง 3 ด้านคือ Knowledge, Skill, Attitude
Educational principles of OSCE
ประกอบไปด้วย Objective และ Structure
Objective
- Standardized scoring rubrics ต้องทำให้เป็น standard
- Trained examiner asking the same question to every candidate เพื่อลด bias
Structure
- Standard station design assessing a specific clinical task ต้องเป็นเรื่องเดียวกัน และชัดเจนว่าจะประเมินอะไร
- Blueprint of curriculum จะต้องดูว่าการออกข้อสอบจาก Curriculum จะประเมินด้วยเครื่องมือชนิดไหนเช่น ถ้า Abdominal pain จะประเมินการตรวจร่างกาย ให้เอาไปทำ OSCE แต่ถ้าจะถามเรื่อง โรคจาก Abdominal pain ให้ไปออก MCQ เนื่องจาก OSCE จะเน้น Clinical competency
- Utility of assessment ต้องคำนึงถึง Validity, Reliability, Feasibility & Acceptability, Educational impact กับนักเรียน
Validity, Reliability and Feasibility
เครื่องมือการประเมินทุกชนิดจะมีข้อดี-ด้อย แตกต่างกันไปในความสามารถทั้งสามด้านดังกล่าวข้างต้นโดย คุณสมบัติเครื่องมือการประเมินของ OSCE ในแต่ละด้านจะเป็นดังนี้
Validity
- จะมี Validity ก็ต้อง matching กับ curriculum และประเมิน Clinical competency
Reliability
- Station พอไหม
- Standardized scoring หรือเปล่า
- Examiners ได้รับการฝึกมาหรือป่าว
- ผู้ป่วยจำลองได้มาตรฐานหรือไม่
Feasibility
- ถือเป็นข้อด้อยของ OSCE ใช้ทรัพยากรมาก ไม่ว่าจะเป็น คน และอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ
Educational impact
- การสอบสามารถกระตุ้นในการเรียนรู้ให้แก่ผู้เรียน ผู้เรียนจะต้องไปฝึกทักษะต่างๆ มาก่อน
OSCE Step-by-Step
การออกข้อสอบ OSCE หากมองในมุมที่กว้างมากขึ้นมีรายละเอียดมากกว่าการออกข้อสอบเพียงอย่างเดียว เนื่องจากการสอบ OSCE เป็นการสอบที่ใช้ทรัพยากรมาก ดังที่กล่าวไปข้างต้น ต้องใช้ทั้งอาจารย์คุมสอบ เจ้าหน้าที่ อุปกรณ์และสถานที่ เพราะฉะนั้นการมี Team ที่ดีในการช่วยบริหารจัดการจะช่วยให้การสอบ OSCE ประสบความสำเร็จได้มากขึ้น
Organizational Team
เป็นที่นำองค์กร/ผู้บริหารองค์กร มีหน้าที่คอยอำนวยความสะดวกหรือช่วยเหลือในด้านทรัพยากรต่างๆ ตั้งแต่การจัดสร้างสถานที่, การจัดซื้ออุปกรณ์ต่างๆ, การจัดหากำลังคน, ค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ เป็นต้น
Administrative Team
เป็นทีมดำเนินการหลักดูภาพรวมทั้งหมดของการจัดการสอบมีหน้าที่เช่น
- จัดสรรนักเรียนที่จะต้องเข้าสอบลงสู่สนามสอบต่างๆ
- แจกจ่ายงานเอกสารต่างๆ ทั้งตัวข้อสอบ และเอกสารประกอบอื่นๆ
- ดำเนินการเรื่องผลการสอบ
จากหน้าที่หลักๆ ข้างต้น จะเห็นว่าเป็นทีมสำคัญ หรือทีมหลักของการจัดการสอบเพราะฉะนั้นจะมีรายละเอียดแต่ละหน้าที่ย่อยๆ อีกดังนี้
Developing the lager team พัฒนาทีม
- หน้าที่นี้จะขึ้นอยู่กับว่าจะต้องขยายทีมหรือไม่ โดยพิจารณาจากข้อสอบ ผู้เข้าสอบ และสถาบัน
- เลือกผู้คุมสอบ, ผู้ป่วยจำลอง, วางระบบวงจรการสอบ OSCE เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าจะไม่มีปัญหาต่างๆ เช่น การเว้นฐานพัก, การเรียงลำดับโจทย์คำถามกับ Station ข้อสอบ หรือการวางแผนแก้ปัญหาล่วงหน้า เป็นต้น
Setting the examination schedule เป็นหน้าที่หลักของทีม Admin ที่จะต้องจัดตารางวันสอบ
Setting an examination blueprint เพื่อให้ชัดเจนว่าจะมีการจัดสอบอะไรบ้าง และประเมินในด้านไหน (เห็นภาพรวมของการสอบ)
ตัวอย่าง Blueprint
| Topics | Procedural skills | Clinical examination skills | History taking | Total number of questions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute medicine | Q.1 | 1 | ||
| ENT | Q.2 | Q.4 | 4 | |
| Q.3 | Q.5 | |||
| Pediatrics | Q.6 | 2 | ||
| Q.7 | ||||
| Geriatrics | Q.8 | Q.10 | 3 | |
| Q.9 | ||||
| Total number of questions | 3 | 4 | 3 | 10 |
Setting an examination length จำนวน Station
- โดยปกติ OSCE จะแบ่งเป็น station ที่สามารถเข้าได้ครั้งเดียว มีเวลาจำกัดต่อ station 5-10 นาที
- เพื่อให้มี reliability อย่างน้อยควรจะจัดให้มี 14-18 stations
Developing a bank of a OSCE station ทีม Admin ควรจัดให้มีคลังข้อสอบ โดยคลังข้อสอบมีการเก็บรายละเอียดข้อมูลแต่ละ station ไว้อย่างละเอียด พร้อมทั้งแบ่งแยกเป็นประเภทของแต่ละ station
ตัวอย่าง Station type สำหรับประกอบการจัดเก็บฐานข้อมูลข้อสอบ
| Station type | Description | Examples | Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed station | An examiner is present throughout the duration of testing | Communication skills, Procedural skills, Clinical examination | Direct observation allows assessment of the higher levels of the learning domains. Immediate feedback can be given for formative assessment. | Resource intensive with one examiner needed per station |
| Unobserved station | No examiner present throughout the testing period. Answers may be submitted on paper either after each station or following the completion of the examination. | Interpretation of clinical information e.g. X-rays, pathology specimens, blood results. Prescribing skills. Information Technology Skills. | Examiners not required on such stations. | No direct observation of performance. OSCE station may not be necessary and alternative assessment tools may be as effective at assessing the cognitive skills in question. |
| Technology enhanced station | A station involving the use of technological advances such as part- task trainers or high- fidelity manikins to assess skills that would otherwise be difficult to assess in the OSCE format. | Intimate clinical examinations with use of part task trainers, e.g. rectal examination. Complex decision making skills and the management of acutely unwell patients with the use of high-fidelity manikins. | Increases the scope of potential OSCE stations, allowing assessment of learning domains which could not be assessed effectively using traditional OSCE stations. | Personnel must be trained in the use of the equipment. Equipment failure. Initial cost of new equipment and maintenance costs. |
| Linked station | Two consecutive stations are based upon the same clinical scenario or information. These may be observed or unobserved. | Unobserved documentation of findings and management plan in the second station. | Greater number of skills can be assessed per scenario. Efficient use of examiner resources. | Needs careful circuit planning, as candidates can neither start on the second of a pair of linked stations nor end the examination on the first. |
การจัดเก็บลองฐานข้อมูลจะต้องใช้ Template ที่ชัดเจน เพื่อให้สามารถสืบค้น และดูแลรักษาต่อเนื่องได้ โดยทีม Admin จะต้องกำหนดการสร้าง Template ที่ชัดเจน เพื่อการเก็บลงฐานข้อมูลนี้
ตัวอย่าง Template
Author
AQ
Subject/Topic
Asthma
Level of the Candidate (choose at least 1)
[x] Year 3
[ ] Year 4
[x] Year 5
Competencies (Essential Field)
Please choose 1 to 3
[x] Clinical Examination Skills
[ ] Communication & Consultation Skills
[x] History Taking
[ ] Hand Over Skills
[ ] Procedural Skills
[ ] Mental Health Assessment
[ ] Professionalism
[x] Application of Knowledge
[ ] Prescription
[ ] Data Interpretation
[ ] Diagnostic Skills
[ ] Management Planning
[ ] Ethics
Station Duration (please do not modify this field)
8 min
SP age & sex
Mark/Mary Freeman, age 32
Resource & Equipment needed
1. Paper and pen, in case the candidate wishes to make notes
2. Alcogel
3. Couch for the patient
4. Stethoscope
5. Water bottle and glasses
Setting up the station
1. Examiner’s chair should be positioned so that he/she can observe faces of both candidate and simulated patient.
2. No desk or table is necessary. If one is present, it should NOT form a barrier between the candidate and the patient.
Brief Background to the scenario
Mark/Mary Freeman is a 32-year-old patient who is attending for their annual asthma review.
Examiner’s Role
Your role is to observe the history taking process and to assess the candidate's examination of the respiratory system
What are the objectives of the station or what is expected of the candidate?
- The candidate is expected to take a brief, focused asthma history from this patient to assess his/her asthma control and make to suggestions as appropriate.
- The candidate is also expected to examine this patient's chest.
The candidate has NOT been asked to take detailed history or perform a general physical examination.
What information they might be able to provide the candidate?
- If the candidate attempts to perform a general physical examination, please ask them to move on to examining the chest.
- If candidates attempt to perform tactile vocal fremitus and whispering pectoriloquy please ask them to omit these and move on.
What information they should not provide the candidate?
- Please do not repeat instructions to the candidate.
- Please do not interrupt or prompt candidate or ask any questions
Clinical information relevant to the station
Key points in Asthma history taking;
1. Onset
2. Duration
3. Family History
4. Occupation
5. Smoking history
6. Housing, soft toys
7. Aggravating and relieving factors, e.g. exercise, weather, allergies, etc.
8. Cough
9. Wheeze
10. Perennial versus Seasonal
11. Diurnal variation/night time symptoms
12. Affect on life style
13. Hospital admissions
14. Treatment including steroids
Key Points in Examination of the Respiratory System;
(A good student would complete the examination at the front before moving to the back)
1. Proper exposure
2. Inspection for symmetry and shape
3. Palpitation of trachea, chest expansion (vocal fremitus not necessary in this case)
4. Percussion, front and back including the clavicles
5. Auscultation at front and back, (whispering pectoriloquy not necessary in this case)
Simulated Patient Information
Who they are?
Mark/Mary Freeman, age 32
Their social/economic background if applicable?
- You are currently working in a telesales call centre (trying to sell fitted kitchens)
- You live in your own small terraced house, with your partner and one daughter
- You bought your daughter a cat 4 months ago (for her birthday)
- Your partner smokes 20 a day and you smoke occasionally - when you go out socialising. You know you shouldn't, but you don't think an occasional one harms your chest. You've been doing this since you were 16
- You have 2-3 drinks (pints of beer or large glasses of wine) when out socialising - which is once a week or less often
- You go to the gym very occasionally
- Your mood is normal (not anxious or depressed)
History
- You have had Asthma most of your life - you think ti was diagnosed when you were about 5 or 6
- It seemed to be much worse as a child - you had been under a hospital clinic, but you have never had to stay in hospital
- As a teenager, ti seemed to go much better - you rarely seemed to need treatment
- In your adult years, ti hasn't troubled you too much, though you have always liked to have a blue inhaler (salbutamol) handy, just in case • fI asked, you have never taken a course of steroid tablets by mouth and you do not own your peak flow meter
- One inhaler usually lasted you several months, as you only needed ti every few days (but see below for current situation). When you use it, you take 2puffs at a time (as instructed), which relieves the coughing and wheezing noises within 5 min or so)
- You have an elder brother with asthma, a your daughter has mild eczema and your father has had hay fever all his life
- Your asthma is not seasonal
- It does not vary by day or night
Details of their concerns/perceptions
- You also wonder if the cat might be to blame. On the other hand, you had a dog when you were young, which didn't affect you, so you don't think you are allergic to animal fur
- You are not really worried about your asthma - you don't think it's anything serious, but you're happy to come for a check-up
What they should say (their agenda) & what they should not say
You think the reason why your asthma is worse is because of working longer hours. There is a fair amount of stress at work, as the company's sales are not doing well. You don't feel that you are getting over-stressed; it's just the general atmosphere at work
What they should ask (questions)
Please do not ask any questions
Specific Standardization issues (specific answer to specific questions, please stay with the script)
If the candidate asks for your thoughts about why your asthma has worsened very early on (before making any effort to establish rapport), say you believe it's the stress at work. But if the candidate asks the same question when you have established some rapport, mention your belief about it being the stress at work, but also say: It's been ever since my daughter's birthday, I suppose. If they probe why you think that might be, mention the cat.สิ่งสำคัญของการทำคลังข้อสอบ OSCE คือ
- Peer review workshops (นำข้อสอบเก่าๆ มาตรวจสอบอีกครั้ง)
- Piloting (ข้อสอบใหม่ ไปทดลองใช้งาน)
- Psychometric analysis (สร้างทีมมาประเมินข้อสอบในคลัง)
Choosing a scoring rubric and standard setting เป็นการกำหนดเกณฑ์การให้คะแนนในแต่ละข้อ และเกณฑ์ผ่านการสอบ
ตัวอย่างเกณฑ์การให้คะแนน
- Checklist binary (ทำหรือไม่ทำ)or rating scale
- Global rating scale (Holistic scoring) ประเมินโดยภาพรวมทั้งหมดไม่เกี่ยวกับคะแนนข้างต้น _หากผลการประเมินใน ข้อ Checklist กับ Global rating scale ขัดแย้งกันอาจจะต้องทบทวนข้อสอบใหม่อีกครั้ง
- Stand setting กำหนดเกณฑ์ว่าจะใช้เกณฑ์อะไร เท่าไรในการคำนวณคะแนนว่าจะผ่านหรือตก
Binary checklist
| ขั้นตอนการประเมิน | สมบูรณ์ | บกพร่อง | ผิด/ไม่ทำ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1…… | 10 | 6 | 0 |
| 2….. | 8 | 4 | 0 |
| 3….. | 5 | 0 | |
| 4….. | 3 | 0 |
Global rating scale
| ระดับ | ดีมาก | ดี | ไม่แน่ใจ | ไม่ได้ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| โปรดประเมินความเห็นของท่าน ถ้าผู้สอบรายนี้นำไปปฏิบัติจริงกับผู้ป่วย (ไม่มีคะแนน) |
Trained Examiners
ลักษณะที่สำคัญของผู้คุมสอบที่ดี คือจะต้องเข้าใจ วัตถุประสงค์ของการคุมสอบ OSCE และสามารถที่จะ Feedback ข้อสอบ เพื่อเกิดประโยชน์ต่อการพัฒนาได้
หน้าที่ของทีม Admin คือ
- Identification of potential examiners เพื่อหาคนที่มีคนใหม่ๆ จะคุมสอบได้
- Training workshop จะต้องจัดเพื่อสอนการคุมสอบ
ลักษณะที่ดีของผู้คุมสอบ
- เข้าใจหลักการและเป้าหมายของการสอบ OSCE
- เข้าใจการใช้ Rubric score ในการให้คะแนนอย่างมีมาตรฐาน
- สามารถเขียน Feedback ให้แก่ผู้เข้าสอบได้ในกรณี summative
- สามารถให้ข้อพัฒนา (verbal) ให้แก่ผู้เข้าสอบในกรณี formative
- สามารถเก็บรักษาความลับของผู้เข้าสอบได้
- รู้เท่าทันพฤติกรรมที่ไม่เหมาะสม หรืออันตรายของผู้เข้าสอบได้
Standardize Patients
ผู้ป่วยจำลอง ประกอบด้วย ผู้ป่วยที่เป็นผู้ป่วยจริงๆ (มีโรคจริง) หรือผู้ป่วยที่ถูกฝึกสอนให้มีความสามารถในการเป็นผู้ป่วยจำลอง โดยจะต้องจัดให้มีมาตรฐาน (Standardize)
Examination Boards
ทีมใหญ่ที่คอยตรวจสอบผลคะแนน และตัดสินเหตุการณ์ต่างๆ
Candidates/Students
องค์ประกอบหลักของ OSCE ที่จะขาดไม่ได้ ก็คือผู้เข้าสอบ
Running the OSCE
ขั้นตอนการจัดสอบ OSCE
Choosing as OSCE venue
ขั้นตอนแรกอาจจะเริ่มง่ายๆ ที่การจัดสถานที่
- Station room ห้องที่จะจัด station
- Waiting room of patients and examiners ห้องพักคอยสำหรับผู้ป่วยและผู้คุมสอบ
- Briefing room ห้องสำหรับแนะนำการสอบแก่ผู้เข้าสอบ
- Administrative room ห้องสำหรับทีม Admin ในการควบคุมและติดตามการสอบ
Setting up the OSCE circuit and equipment
- The OSCE circuit วงจร OSCE หรือการจัดทิศทางการวนของ station ในแต่ละข้อ
- Circuit with rest station จำนวน station พักต้องมีความเหมาะสม
- Considerations for individual stations ระยะเวลาของแต่ละ station ต้องมีความเหมาะสม
- The equipment อุปกรณ์ต่างๆ เช่น อุปกรณ์สำรอง การตรวจสอบความพร้อม ความครบถ้วน
Examination day briefing
ขั้นตอนการสรุป ข้อมูลที่จำเป็นก่อนการสอบ แก่ทั้งสามกลุ่ม
- Candidate briefing ผู้เข้าสอบ
- Examiners briefing ผู้คุมสอบ
- Standardized patient briefing ผู้ป่วยจำลอง
Candidate briefing
ข้อมูลที่ควรให้แก่ผู้เข้าสอบ
- จำนวน stations ทิศทางการหมุนแต่ละ stations จุดเริ่มต้น, จัดพัก
- ทบทวนกฏและระเบียบการสอบ
- การกักตัว (ถ้ามี)
Examiners briefing
ข้อมูลต่างๆ ที่ควรให้แก่ผู้คุมสอบ
- วัตถุประสงค์ของการสอบ เช่น Formative หรือ Summative
- ตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของนักเรียนในแต่ละ station เช่น ถูกชื่อ ถูกคน
- วิธีการให้คะแนน
- เน้นความสำคัญของการรักษาความลับทั้ง station และการให้คะแนน
- ไม่อนุญาตให้พูดกับผู้เข้าสอบมากเกินกว่าที่กำหนดไว้
- คุมสอบโดยปฏิบัติเหมือนกันกับผู้เข้าสอบทุกคน
- วิธีการรายงานข้อกังวล หรือสงสัยสำหรับผู้เข้าสอบ
- ให้ข้อมูล Feedback หลังการสอบ
Standardise patient briefing
ผู้ป่วยจำลองจะเน้นที่ความสำคัญของการเป็นมาตรฐานที่เท่าเทียมกันให้กับผู้เข้าสอบทุกคน มีความสามารถในการให้ข้อมูล feedback และท้ายที่สุดเป็นเรื่องการบริหารจัดการเช่น ระยะเวลาการพัก หรือสิ่งอำนวยความสะดวกต่างๆ